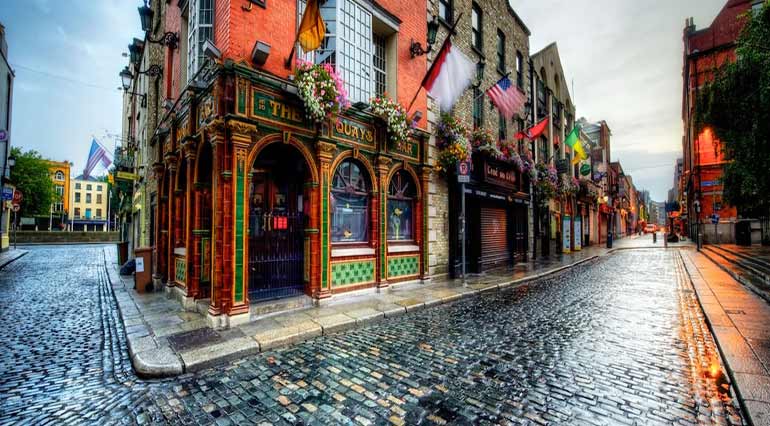
Ireland, is an island to the north-west of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth. To its east is the larger island of Great Britain, from which it is separated by the Irish Sea.

Full name: Republic of Ireland
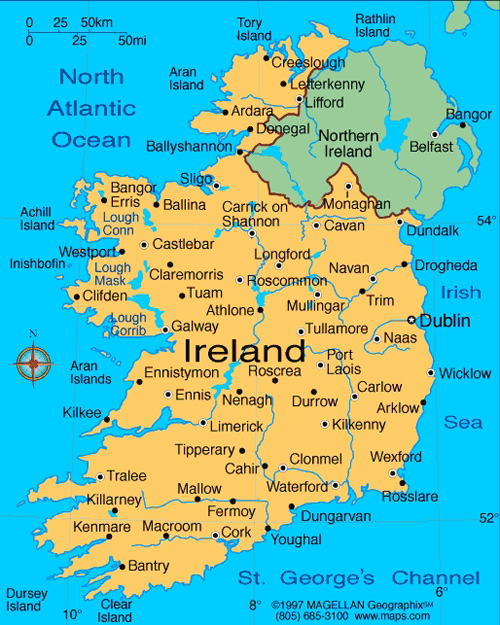
Capital: Dublin
Area: 70.273 km2
% Water: 2 %
Popolulation: 4.588.252
Density: 65,2/km2
Continent: Europe
Valuta: Euro
Politically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland, which covers just under five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, a part of the United Kingdom, which covers the remainder and is located in the north-east of the island. The population of Ireland is approximately 6.4 million. Just under 4.6 million live in the Republic of Ireland and just under 1.8 million live in Northern Ireland.

Relatively low-lying mountains surrounding a central plain epitomise Ireland’s geography with several navigable rivers extending inland. The island has lush vegetation, a product of its mild but changeable oceanic climate, which avoids extremes in temperature. Thick woodlands covered the island until the 17th century. Today, it is one of the most deforested areas in Europe. There are twenty-six extant mammal species native to Ireland.

A Norman invasion in the Middle Ages gave way to a Gaelic resurgence in the 13th century. Over sixty years of intermittent warfare in the 1500s led to English dominance after 1603. In the 1690s, a system of Protestant English rule was designed to materially disadvantage the Catholic majority and Protestant dissenters, and was extended during the 18th century. In 1801, Ireland became a part of the United Kingdom. A war of independence in the early 20th century led to the partition of the island, creating the Irish Free State, which became increasingly sovereign over the following decades. Northern Ireland remained a part of the United Kingdom and saw much civil unrest from the late 1960s until the 1990s. This subsided following a political agreement in 1998. In 1973, both parts of Ireland joined the European Economic Community.

Irish culture has had a significant influence on other cultures, particularly in the fields of literature and, to a lesser degree, science and education. A strong indigenous culture exists, as expressed for example through Gaelic games, Irish music and the Irish language, alongside mainstream Western culture, such as contemporary music and drama, and a culture with much in common with Great Britain, as expressed through sports such as soccer, rugby, horse racing, and golf, as well as the English language.

Geography
The island of Ireland is located in the north-west of Europe, between latitudes 51° and 56° N, and longitudes 11° and 5° W. It is separated from the neighbouring island of Great Britain by the Irish Sea and the North Channel, which has a width of 23 kilometres (14 mi) at its narrowest point. To the west is the northern Atlantic Ocean and to the south is the Celtic Sea, which lies between Ireland and Brittany, in France. Ireland and Great Britain, together with nearby islands, are known collectively as the British Isles. As the term British Isles is controversial in relation to Ireland, the alternate term Britain and Ireland is often used as a neutral term for the islands.

A ring of coastal mountains surround low plains at the centre of the island. The highest of these is Carrauntoohil (Irish: Corrán Tuathail) in County Kerry, which rises to 1,038 m (3,406 ft) above sea level. The most arable land lies in the province of Leinster. Western areas can be mountainous and rocky with green panoramic vistas. The River Shannon, the island’s longest river at 386 km (240 mi) long, rises in County Cavan in the north west and flows 113 kilometres (70 mi) to Limerick city in the mid west.

The island’s lush vegetation, a product of its mild climate and frequent rainfall, earns it the sobriquet the Emerald Isle. Overall, Ireland has a mild but changeable oceanic climate with few extremes. The climate is typically insular and is temperate avoiding the extremes in temperature of many other areas in the world at similar latitudes. This is a result of the moderating moist winds which ordinarily prevail from the South-Western Atlantic.
Precipitation falls throughout the year but is light overall, particularly in the east. The west tends to be wetter on average and prone to Atlantic storms, especially in the late autumn and winter months. These occasionally bring destructive winds and higher total rainfall to these areas, as well as sometimes snow and hail. The regions of north County Galway and east County Mayo have the highest incidents of recorded lightning annually for the island, with lightening occurring approximately five to ten days per year in these areas. Munster, in the south, records the least snow whereas Ulster, in the north, records the most.

Inland areas are warmer in summer and colder in winter. Usually around 40 days of the year are below freezing 0 °C (32 °F) at inland weather stations, compared to 10 days at coastal stations. Ireland is sometimes affected by heat waves, most recently in 1995, 2003 and 2006. In common with the rest of Europe, Ireland experienced unusually cold weather during the winter of 2009/10. Temperatures fell as low as −17.2 °C (1 °F) in County Mayo on December 20 and up to a metre (3 ft) of snow in mountainous areas.

The island consists of varied geological provinces. In the far west, around County Galway and County Donegal, is a medium to high grade metamorphic and igneous complex of Caledonide affinity, similar to the Scottish Highlands. Across southeast Ulster and extending southwest to Longford and south to Navan is a province of Ordovician and Silurian rocks, with similarities to the Southern Uplands province of Scotland. Further south, along the County Wexford coastline, is an area of granite intrusives into more Ordovician and Silurian rocks, like that found in Wales. In the southwest, around Bantry Bay and the mountains of Macgillicuddy’s Reeks, is an area of substantially deformed, but only lightly metamorphosed, Devonian-aged rocks. This partial ring of “hard rock” geology is covered by a blanket of Carboniferous limestone over the centre of the country, giving rise to a comparatively fertile and lush landscape. The west-coast district of the Burren around Lisdoonvarna has well-developed karst features. Significant stratiform lead-zinc mineralisation is found in the limestones around Silvermines and Tynagh.
Hydrocarbon exploration is ongoing following the first major find at the Kinsale Head gas field off Cork in the mid-1970s. More recently, in 1999, economically significant finds of natural gas were made in the Corrib Gas Field off the County Mayo coast. This has increased activity off the west coast in parallel with the “West of Shetland” step-out development from the North Sea hydrocarbon province. The Helvick oil field, estimated to contain over 28 million barrels (4,500,000 m3) of oil, is another recent discovery.
Demography
People have lived in Ireland for over 9,000 years, although only a limited amount is known about the palaeolithic, neolithic and Bronze Age inhabitants of the island. Early historical and genealogical records note the existence of dozens of different peoples that may or may not be mythological, for example the Cruithne, Attacotti, Conmaicne, Eóganachta, Érainn, and Soghain, to name but a few. Over the past 1000 years or so, Vikings, Normans, Scots and English have all added to the Gaelic population and have had significant influences on Irish Culture.

Ireland’s largest religious group is Christianity. The largest denomination is Roman Catholicism representing over 73% for the island (and about 87% of the Republic of Ireland). Most of the rest of the population adhere to one of the various Protestant denominations (about 53% of Northern Ireland). The largest is the Anglican Church of Ireland. The Muslim community is growing in Ireland, mostly through increased immigration. The island has a small Jewish community. About 4% of the Republic’s population and about 14% of the Northern Ireland population describe themselves as of no religion. In a 2010 survey conducted on behalf of the Irish Times, 32% of respondents said they went to a religious service more than once a week.
The population of Ireland rose rapidly from the 16th century until the mid-19th century, but a devastating famine in the 1840s caused one million deaths and forced over one million more to emigrate in its immediate wake. Over the following century the population was reduced by over half, at a time when the general trend in European countries was for populations to rise by an average of three-fold.

Culture
Ireland’s culture comprises elements of the culture of ancient immigration and influences (such as Gaelic culture) and more recent Anglicisation and Americanisation as well as participation in a broader European culture. In broad terms, Ireland is regarded as one of the Celtic nations of Europe, which also includes Scotland, Wales, Cornwall, Isle of Mann and Brittany. This combination of cultural influences is visible in the intricate designs termed Irish interlace or Celtic knotwork. These can be seen in the ornamentation of medieval religious and secular works. The style is still popular today in jewellery and graphic art, as is the distinctive style of traditional Irish music and dance, and has become indicative of modern “Celtic” culture in general.
Religion has played a significant role in the cultural life of the island since ancient times (and since the 17th century plantations, has been the focus of political identity and divisions on the island). Ireland’s pre-Christian heritage fused with the Celtic Church following the missions of Saint Patrick in the 5th century. The Hiberno-Scottish missions, begun by the Irish monk Saint Columba, spread the Irish vision of Christianity to pagan England and the Frankish Empire. These missions brought written language to an illiterate population of Europe during the Dark Ages that followed the fall of Rome, earning Ireland the sobriquet, “the island of saints and scholars”. In more recent years, the Irish pubs have become outposts of Irish culture worldwide.

The Republic of Ireland’s national theatre is the Abbey Theatre founded in 1904 and the national Irish-language theatre is An Taibhdhearc, established in 1928 in Galway. Playwrights such as Seán O’Casey, Brian Friel, Sebastian Barry, Conor McPherson and Billy Roche are internationally renowned.
Cuisine
Food and cuisine in Ireland takes its influence from the crops grown and animals farmed in the island’s temperate climate and from the social and political circumstances of Irish history. For example, whilst from the Middle Ages until the arrival of the potato in the 16th century the dominant feature of the Irish economy was the herding of cattle, the number of cattle a person owned was equated to their social standing. Thus herders would avoid slaughtering a milk-producing cow.
For this reason, pork and white meat were more common than beef and thick fatty strips of salted bacon (or rashers) and the eating of salted butter (i.e. a dairy product rather than beef itself) have been a central feature of the diet in Ireland since the Middle Ages. The practice of bleeding cattle and mixing the blood with milk and butter (not unlike the practice of the Maasai) was common and black pudding, made from blood, grain (usually barley) and seasoning, remains a breakfast staple in Ireland. All of these influences can be seen today in the phenomenon of the “breakfast roll”.

The introduction of the potato in the second half of the 16th century heavily influenced cuisine thereafter. Great poverty encouraged a subsistence approach to food and by the mid-19th century the vast majority of the population sufficed with a diet of potatoes and milk. A typical family, consisting of a man, a woman and four children, would eat 18 stone (110 kg) of potatoes a week. Consequently, dishes that are considered as national dishes represent a fundamental unsophistication to cooking, such as the Irish stew, bacon and cabbage, boxty, a type of potato pancake, or colcannon, a dish of mashed potatoes and kale or cabbage.
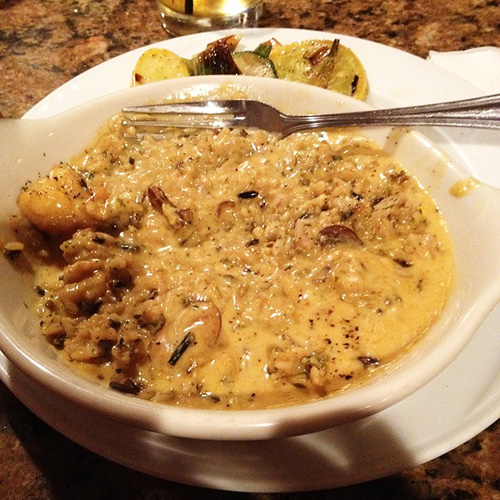

Since the last quarter of the 20th century, with a re-emergence of wealth in Ireland, a “New Irish Cuisine” based on traditional ingredients incorporating international influences has emerged. This cuisine is based on fresh vegetables, fish (especially salmon, trout, oysters, mussels and other shellfish), as well as traditional soda breads and the wide range of hand-made cheeses that are now being produced across the country. The potato remains however a fundamental feature of this cuisine and the Irish remain the highest per capita consumers of potatoes in Europe. An example of this new cuisine is “Dublin Lawyer”: lobster cooked in whiskey and cream. Traditional regional foods can be found throughout the country, for example coddle in Dublin or drisheen in Cork, both a type of sausage, or blaa, a doughy white bread particular to Waterford.
Drink
Since the last quarter of the 20th century, with a re-emergence of wealth in Ireland, a “New Irish Cuisine” based on traditional ingredients incorporating international influences has emerged. This cuisine is based on fresh vegetables, fish (especially salmon, trout, oysters, mussels and other shellfish), as well as traditional soda breads and the wide range of hand-made cheeses that are now being produced across the country. The potato remains however a fundamental feature of this cuisine and the Irish remain the highest per capita consumers of potatoes in Europe. An example of this new cuisine is “Dublin Lawyer”: lobster cooked in whiskey and cream. Traditional regional foods can be found throughout the country, for example coddle in Dublin or drisheen in Cork, both a type of sausage, or blaa, a doughy white bread particular to Waterford.
Ireland once dominated the world’s market for whiskey, producing 90% of the world’s whiskey at the start of the 20th century. However, as a consequence of bootleggers during the prohibition in the United States (who sold poor-quality whiskey bearing Irish-sounding names thus eroding the pre-prohibition popularity for Irish brands) and tariffs on Irish whiskey across British Empire during the Anglo-Irish Trade War of the 1930s, sales of Irish whiskey worldwide fell to a mere 2% by the mid-20th century. In 1953, an Irish government survey, found that 50 per cent of whiskey drinkers in the United States had never heard of Irish whiskey.

Irish whiskey, however, remained popular domestically and in recent decades has grown in popularity again internationally. Typically, Irish whiskey is not as smoky as a Scotch whisky, but not as sweet as American or Canadian whiskies. Whiskey forms the basis of traditional cream liqueurs, such as Baileys, and the “Irish coffee” (a cocktail of coffee and whiskey reputedly invented at Foynes flying-boat station) is probably the best-known Irish cocktail.
Stout, a kind of porter beer, particularly Guinness, is typically associated with Ireland, although historically it was more closely associated with London. Porter remains very popular, although it has lost sales since the mid-20th century to lager. Cider, particularly Magners (marketed in the Republic of Ireland as Bulmers), is also a popular drink. Red lemonade, a soft-drink, is consumed on its own and as a mixer, particularly with whiskey.


